Ischemia Definition
Ischemia is the result when there is inadequacy in blood flow causing an insufficiency in oxygen and nutrient that is vital for cellular metabolism due to restriction in blood supply. Restriction in blood supply brought subsequent damage or dysfunction to tissues. Ischemia is said to be due to blood vessels problem.
picture 1: Ischemia in the artery of Heart which leads to heart attack.
image source: heartsmartnow.com
Ischemia Time
In transplantation surgery, an organ or body part pulled out of the body has been temporarily cut off with blood supply and oxygen. Supply of blood and oxygen is vital to tissue, organ and body parts to maintain and keep it from functioning. Starvation from oxygen of tissues and organs in a period of twenty minutes will cause it to have irreversible damage.Transplantation procedure requires two types of ischemic time which is very vital to maintain and keep the organ alive during the time of blood perfusion. Ischemic time types are:
Warm Ischemic Time is applying a room temperature to an organ or tissue after blood supply and oxygen has been cut off. The warm ischemic time is applied in two periods wherein one period is applied during retrieval of an organ from cross clamping until cold perfusion commenced while the other period is applied during implantation when the organ is removed from ice until reperfusion.
Cold Ischemic Time is the process of keeping the organ chilled during the absence of blood and oxygen supply while the organ is in transport and on standby for reperfusion. The organ is cooled down with a use of cold perfusion solution after it is removal during implantation procedure.
Cold ischemic time ends after the tissue reaches its physiological temperature when warm ischemic time begins until the completion of surgical procedure.
Types of Ischemia
Ischemia can happen to any part of the body. It can be described as acute or chronic. Acute ischemia is described to occur suddenly and requires immediate medical intervention or attention. Chronic ischemia on the other hand occurs over time and mostly to people with other underlying condition such as diabetes.Pain is often the symptom of ischemia although an ischemia may occur without manifesting pain or even any warning and this is called silent ischemia.
Ischemia occurs more often and can be classified according to the location they occur and these are:
Myocardial Ischemia occurs when there is a decrease in the blood flow to the heart muscle whether by partial or complete blockage of the artery. Damage to the heart muscle due to ischemia can hamper or reduce the ability of the heart muscle to pump blood efficiently and blockage in the coronary artery may lead to heart attack.The occurrence of myocardial ischemia may happen slowly when arteries are blocked overtime or may also occur abruptly when there is sudden blockage in the artery.
Cerebral Ischemia or brain ischemia occurs when there is insufficient oxygen or blood flow to the brain whether a part of the brain or a wide area in the brain. It is classified as focal when ischemia is confined in one part of the brain. Ischemia in the brain is classified as global when it encompasses a wide area of the brain.
Cerebral ischemia may lead to cerebral hypoxia which when not properly intervened can lead to cerebral infarction or ischemic stroke. Brain cells can die within a minute of oxygen starvation.
picture 2: Cerebral Ischemia which leads to oxygen imabalne in brain.
image source: iahealth.net
Intestinal Ischemia is a decreased blood flow in the intestine which can affect the small intestine or large intestine and can also affect both small and large intestine. This condition is serious and can be fatal. Intestinal ischemia may come in suddenly or slowly occurring overtime. Small intestine ischemia is termed as mesenteric ischemia. Ischemia of the large intestine often leads to inflammatory process known as ischemic colitis.
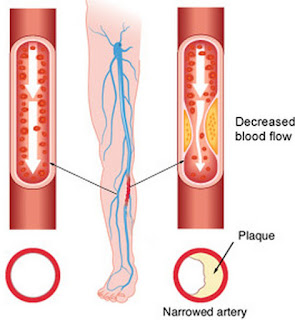
Limb Ischemia is a decreased blood flow in the limb often due to embolism or thrombosis in the artery of patient usually suffering from peripheral vascular disease. The ischemia may suddenly occur and referred as acute limb ischemia which can be treated through surgical procedures. Limb ischemia that requires amputation is in advance stage and is called critical limb ischemia which is due to ischemia associated with gangrene or non-healing ulcers.
picture 3: Limb Ischemia which leads to form Gangerines
image source: stemsupplement.com
Ischemia Symptoms
Symptoms of ischemia vary depending on the affected site of ischemia. The most common symptom of ischemia however, is pain regardless of the affected site.Myocardial Ischemia symptoms:
- Shortness in breath
- Pain in the chest on the left side of the body
- Neck and jaw pain
- Sweaty and clammy skin
- Shoulder and arm pain
- Irregular pulse
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
Cerebral Ischemia symptoms:
- Ischemia within the internal carotid artery will manifest through symptoms like blindness in one eye, weakness in arm or legs and weakness on entire one side of the body.
- Ischemia within the vertebral arteries will manifest with symptoms like dizziness, double vision, vertigo and weakness on both sides of the body.
- Other symptoms include slurred speech, loss of coordination and difficulty speaking.
Intestinal ischemia symptoms depend on onset and these are:
Acute intestinal ischemia:
- Sudden onset of severe abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Abdominal distention
- Urgent bowel movement accompanied with bloody stool
Chronic Intestinal Ischemia:
- Abdominal pain after eating
- Weight loss associated with fear of pain after eating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating
Ischemia Causes
Ischemia is due to factors predisposing an individual to suffer from it and these factors are:- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Vascular disease
- High blood pressure
- Age factor
- Stress
- Overweight or obesity
- Eating habit
- Cigarette smoking
- Physical inactivity
Ischemia Treatment
Treating ischemia is aimed at regulating blood flow to affected area to prevent further damage and these are:- Surgical procedures required in removing and bypassing blocked vessels
- Oxygen therapy
- Drug treatment in preventing clotting
- Medicine to manage pain
- Thrombolytic drugs to dissolve clots
- Blood vessel expansion